|
Database Visualizer
Introduction We start with the note that the "Database Visualizer" is not "Data Visualizer". Data Visualizer: Data visualization is a general term that describes any effort to help people understand the significance of data by placing it in a visual context. Patterns, trends and correlations that might go undetected in text-based data can be exposed and recognized easier with data visualization software. Database Visualizer: The best answer of defining "Database Visualizer" is the following image #1, where the Database Visualizer would either make the existing database system looks like an almost perfect structure or it actually converts the existing database system structure into a more manageable database system. 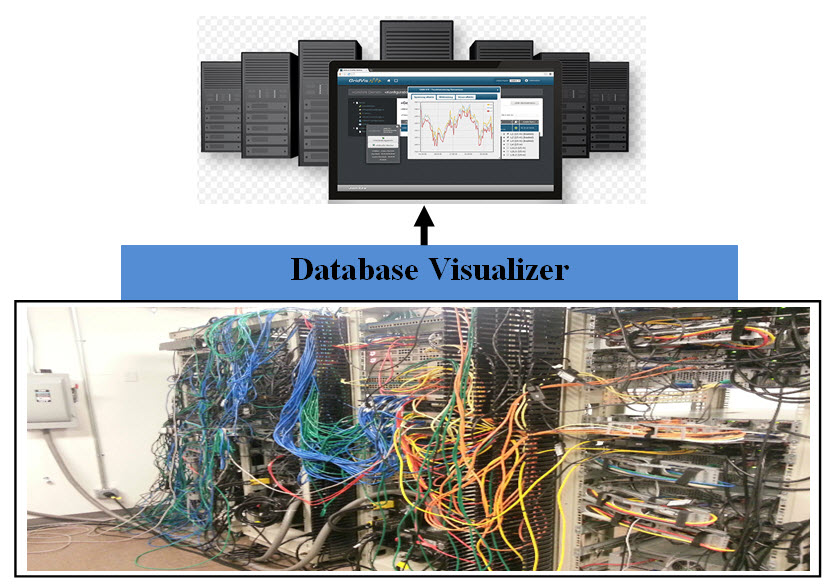
The question is how can we achieve each and the cost in term of effort and time and not to mention testing. Our architect is a Quick Fix Use Case: Building Database Visualizer Description: Our brief description may not be brief since the following points must be addressed. Sadly, most of existing database visualizer in the market are not even close to what the actual database visualizer concept is all about. The top visualizer tools have business features such as BI, Analytics, Dashboard or mobile features, but these visualizer tools do not address how to work with companies data warehouse issues such as:
Briefly Describe This Use Case Working for big name cooperations, most people think that the internal structure and databases are textbook structure. Sadly, the reality is exactly the opposite. We recommend the following approach: Quick Fix Address Security Permanent Solution Quick Fix: The timely conversion to address the performance answer: Address Security: Security must addressed with the quick fix and permanent solution. Permanent Solution: For permanent solution see our Intelligent Metadata approach - http://crmmetadata.com/ site. Primary Actor: Management, development, system admin, offshore support, and actual database software and hardware. Goals: Build a transparent and refactoring layer of services which handles Security, Loosely Coupled, Performance, Redundancy, Errors, Scalability, Expandability, Latency, Flexibility, Intelligence, Reliability and Availability. Analysis Each database has tables, files, stored procedures, schemas, Secure Connection, Server encrypted, Trust Certificate, Query Builder, ..etc. Database space are data blocks, extents, and segments. Therefore creating a Database Visualizer to optimize the databases structure, performance and security is not an easy task unless the data in the database is reformatted in our new XML-IDAO structure. Our analysis are presenting two scenarios, the first is a company with few databases and second it a company such as United Airlines with over 100,000 of different database, plus some are old and still use old technologies. For the small number of database, we recommend using our Intelligent Data access Object for Security - see the link: Intelligent Data access Object for Security Second Scenario - United Airlines: With the assumption that United Airlines may have over 100,000 different databases, plus some are old and they are still using old technologies. We can only recommend Vertical and Horizontal scaling. Also recommend that United runs a number of statistics and create a priority list of database servers which are critical and require Vertical and Horizontal scaling. Vertical Scaling: The vertical scaling is done by increasing the capacities of each database server components such as: CPU More Memory Disk space Database connections pool Storage and SQL Server capacity planning Horizontal Scaling: The horizontal scaling is done by the following: Adding more database if possible (Virtual or Bare-Mental) Using virtualized infrastructure Structure logical clusters Redundancy Load balancing Use temporary virtual clones to handle high load Architect Virtualization, Virtualization, Virtualization and more Virtualization: We are talking about: Virtual Servers (we define them as Sub-Servers Objects in OOD Model ) Virtual Containers Virtual Clusters Virtual Networks Object Oriented System (OOS) or Object Oriented Design (OOD) can be implanted in the following:
Advantage of Virtualization: Network virtualization supports the complex requirements in multi-tenancy environments. Network virtualization can deliver a virtual network within a virtual environment with independent network resources. These virtual network can disperse traffic into zones or containers to ensure traffic balance and resources distribution. Customizing virtual servers and networks to meet the business requirement is the way to go. With Object oriented Design such virtual structured environment would be composed of manageable objects and our OO Virtual Model would be Easy to: Structure and size Build Copy Clone Modify Test Inherit Move around Also such virtualization can be created as a running prototype, or we can build software programs as model virtualizer similar to ones that are used in building airplanes, big buildings or high-rises. Such a program(s) can be created as way to give estimates, be part of the planning as well as test other criteria without building anything. Virtual Networks: A Network is all the running hardware, software, interfaces, wiring, IP addresses, licenses and anything any network requires. In term of Network and Network Management, a network is a handful of hardware, software, interfaces and man-hours which also has the potential of expanding and growing out of control. To convert a network into a class or an object we need to split Virtual Networking into sub-classes: Bare-Metal Sub-Class one of more Bare-Metal Container (actual hardware as the class Attributes) Management Sub-Class one of more Service manager Container Documentation Sub-Class one of more Documentation Container Virtual Network Sub-Class one of more Server Containers Exception Sub-Class Zero of more error tracking and handling Container Change Control Sub-Class Zero of more Change Control Container OS Container What is a Virtual Network Class? A Virtual Network Class (object) is an independently running network and contains all virtual sub-classes listed. A Virtual Network Class can be extended-inherited and reused by other Virtual Network Class. Virtual and Bare-Metal: To clear our virtual concept, every hardware including physical servers, switches, wiring, etc are represented into two forms or ways as: Software Sub-server containing the hardware Properties of virtual classes For example, the firewall hardware or box would be represented or assigned a software Virtual Sub-Server which would be the link and the handler of such hardware. Even if the hardware may be directly handling the traffic, the software Virtual Sub-Server is the representation of the firewall hardware within the Virtual Container as follows: The Firewall Virtual Sub-Servers Methods will have the steps and processes dealing, running and maintaining the firewall hardware or box. The Firewall Virtual Sub-Servers Properties will be the documentation for tracking the wiring, links, and IP addresses and so on. Bare-metal Container would have all the firewall physical boxes and data including the hardware inventory and expiration tracking Technical Notes: As for properties, these can be implemented as a Java ArrayList<String> data type Object which throws an exception when any of these Properties are deleted if such properties are shared between Virtual Containers or networks. For example, routers and switches can be stored or assigned as Properties of a Sub-Server object. They can be also shared between Sub-Servers, containers or even virtual networks. Network and Network Managed Services: The breakdown of the Network and the Management Services and into objects: 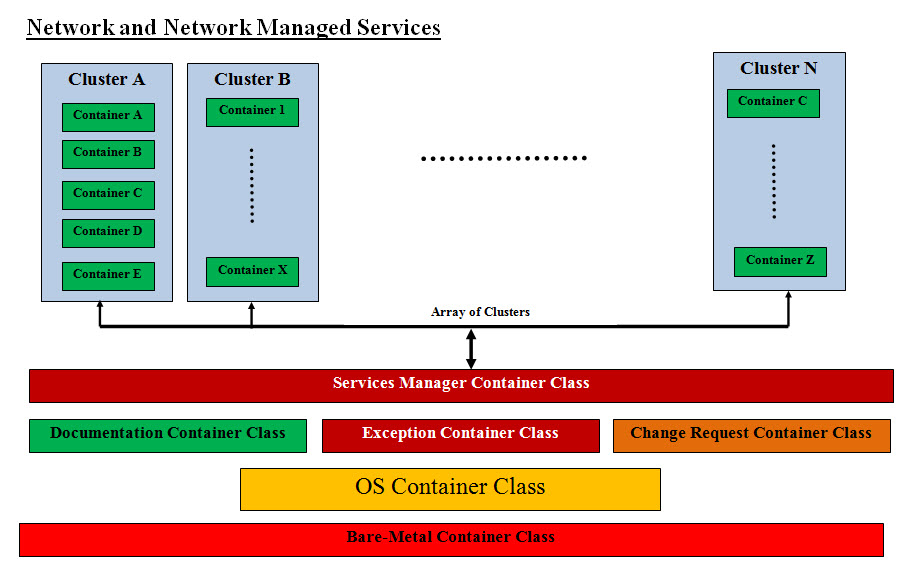
Virtualization and Object Oriented Design Classes Network Engineering and Design High Availability Security Plant Design Installation Sub-Servers and Containers and their properties and methods Network Architecture Firewalls, routers and switches Server Network Interface Card (NIC) Teaming (High Availability Architecture) Load Balancers and Intrusion Detection Systems WAN/LAN Integration and Storage Area Networks (SAN) Telco Services, including Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) Leverage Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) enhanced features and functionality to effectively Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Installation and Configuration Services Services Management Container Skilled Staff Network Utilization Capacity Management Performance and availability management, including eliminating bottlenecks Pro-active preventive management and highly efficient reactive capabilities for unexpected repair problems Contingency plans Documentation Sub-Server and Container User account administration, network devices and configuration, and change management Standard monthly reports, including network services reports and incident reports Exception Container Connectivity troubleshooting and monitoring Automated preventive notification Pre-failure alerting Trend analysis Event correlation and root cause analysis Troubleshooting and Problem Resolution Change Request Container Rigorous change and configuration management, including auto-discovery process and performance thresholds OS Container Network Operations Monitoring, alerting and reporting iPhone Operating System (IOS) Firmware Patch Management Troubleshooting and Problem Resolution Support DIRs customers Bare-Metal Container All the Physical hardware Hardware inventory Hardware expiration tracking Reality Check: Using Object oriented Design and Virtualization in Building Data Centers is new and needs all parties involved to be open-minded, think in these terms (OOD and virtualization) and see the advantages of using these approaches. From experience we may have an uphill battle convincing all the parties involved. Virtual Topology: The key ingredient is our virtual network is the following Containers: Services Managers Container Documentation Container Exception Container Change Control Container These Containers run the show with Services Managers Container as the Kernel or the Boss. They should be built as a Virtual Cluster. The Second key ingredient is the size of these classes or object should be manageable by human with automation and intelligence. Since these Containers or clusters are virtual so creating an array of these cluster would be manageable and can be copied, moved and inherited. We can actually name the Center Structure cluster as Control-Tracking Cluster Class. The same thing can be apply to virtual network in term of size, management and complexity. 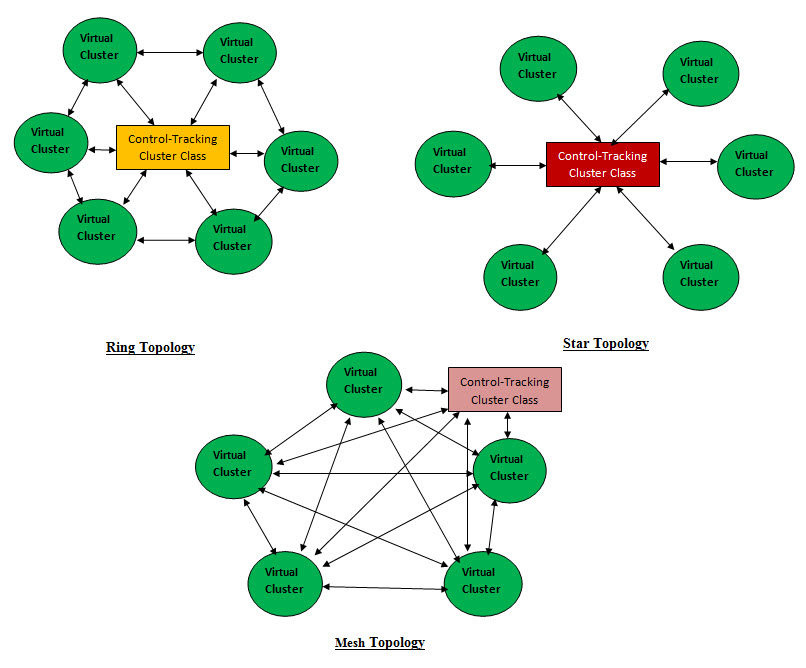
Star Topology Mesh Topology Ring Topology Data Center Specification Network Editor: With same approach we are building cluster editor, we also developing an editor for Network. The difference between these two editors is the network will be using the cluster's data structure-classes and arrays of classes to build the network classes. As for the management and documentation, the Network editor management and documentation classes would be the level higher in the building structure hierarchy. 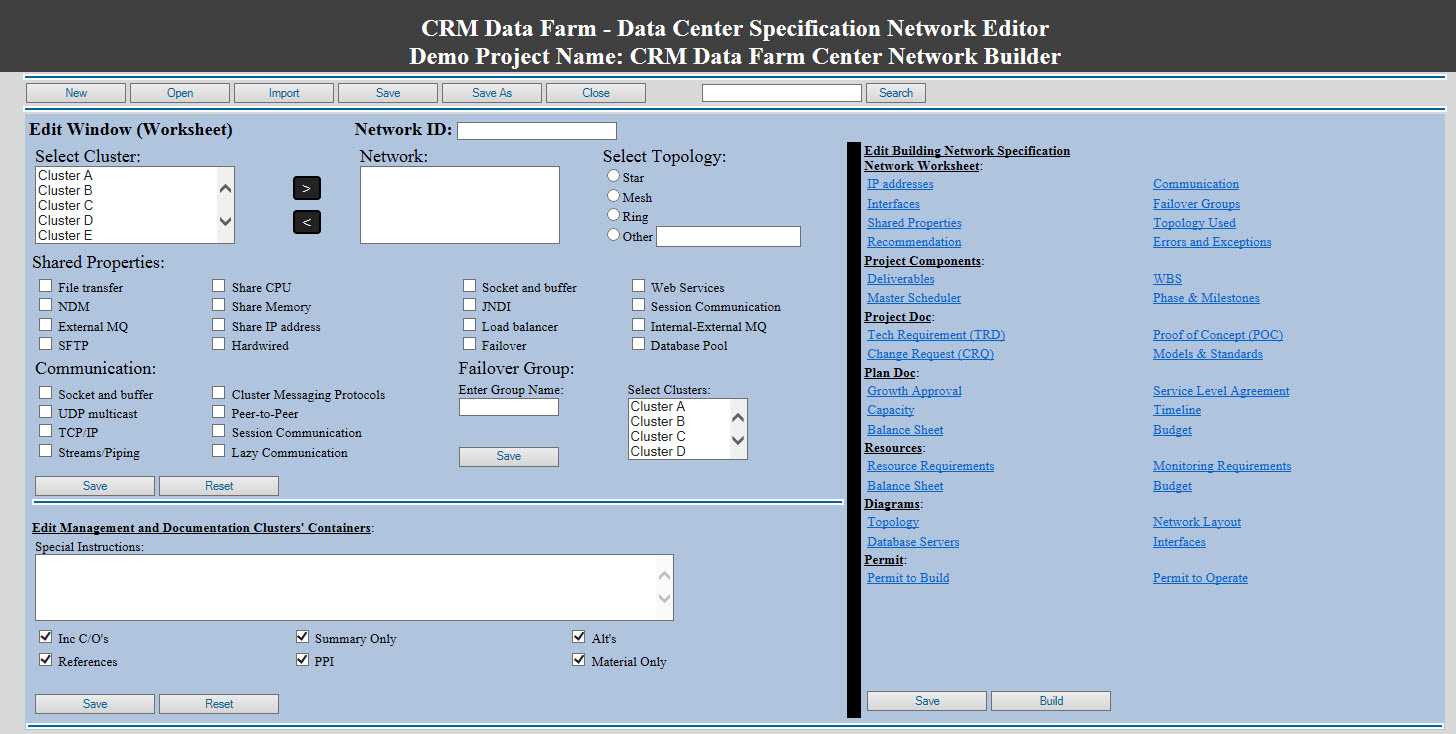
Parallel Arrays of Virtual Network and Control-Tracking Cluster: These can be viewed as parallel arrays first the Virtual Networks array and second is the Control-Tracking Cluster array. An admin GUI interface should be developed as the human control center for all the virtual networks and their supportive Bare-Metal containers. The best answer to our virtual model and approach would be best illustrated with the following topologies: Addressing Security with Virtualization: When it comes to security, Virtualization is a very powerful tool in creating and managing layers of security such as: 1. Virtual Proxy Servers as security front 2. Virtual Firewalls - actual protection and filters 3. Virtual Sandboxing to isolate a number of running software 4. Using Virtualization to create clusters with different functionality - adds a layer of abstraction 5. Isolation and multi-tenancy 6. Virtual Honeypots and Honeynets - decoy and traps 7. Rollback Honeypots are computers set up for the purpose of luring attackers, and a honeynet is an entire network of honeypots. The honeynet looks to the outsider like a production network. |
|---|